Every silicone project starts with uncertainty. Without a clear process window, quality issues and rework are inevitable.
Establishing and validating a process window ensures silicone products move from prototype to mass production with stable quality and consistent performance.
When I managed my first silicone molding project, I learned that early process definition saves time later. Each step — from requirement freeze to PPAP — builds confidence that the final parts will meet design intent and quality goals.
Requirement Freeze and CTQ Definition?
Unclear requirements cause most delays in silicone manufacturing. Vague specifications often lead to mismatched expectations between engineering and production.
Freezing requirements and defining CTQs (Critical to Quality characteristics) set the foundation for process window development.
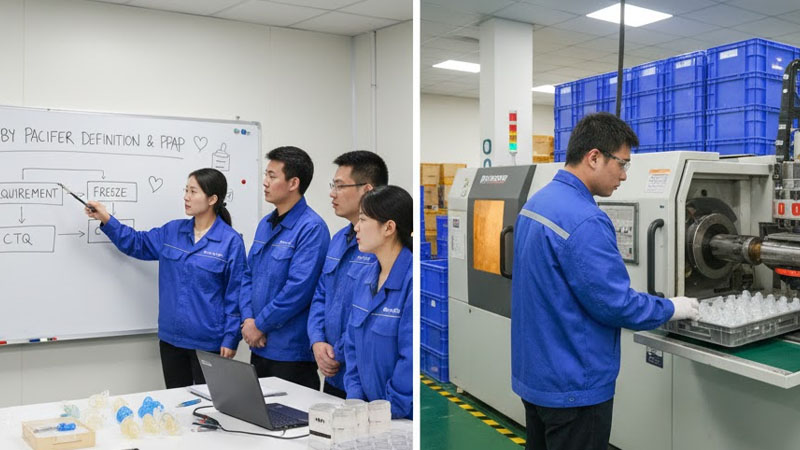

At the start of a project, I sit with the design team to translate functional goals into measurable CTQs. For example, for a baby pacifier, CTQs might include nipple hardness, flash thickness, and bonding strength to the plastic ring.
Steps to Define CTQs
| Step | Action | Output |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Review design drawings | Identify key dimensions |
| 2 | Discuss performance goals | Define measurable indicators |
| 3 | Conduct risk assessment (FMEA) | Prioritize CTQs |
| 4 | Freeze requirements | Document baseline for validation |
Once CTQs are frozen, they guide tooling design, process parameter studies, and quality inspection planning. Any design change after this stage requires formal review to maintain traceability.
DOE and Process Parameter Window?
Without controlled experiments, process limits remain unknown. Guesswork leads to inconsistent quality and long setup times.
Design of Experiments (DOE) identifies key factors affecting silicone molding and defines the process window for stable production.
I remember a project where flash control was inconsistent across cavities. By running a structured DOE on injection speed, mold temperature, and curing time, we discovered that slower injection and higher mold temperature stabilized flow and reduced flash significantly.
Example DOE Structure
| Parameter | Range Tested | Optimal Value | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mold Temp (°C) | 130–170 | 155 | Affects cure and shrinkage |
| Injection Speed (%) | 40–90 | 60 | Controls air entrapment |
| Curing Time (s) | 30–90 | 60 | Balances cycle time and hardness |
After DOE, we establish normal, warning, and out-of-spec zones for each parameter. These ranges define the process window. Operators must set machines within the normal zone, while any drift into the warning zone triggers review.
PPAP and Mass Production Validation?
Process approval cannot rely on lab samples alone. Only verified runs under production conditions prove the window is robust.
Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) confirms that the defined process can produce consistent parts meeting all specifications.

For silicone molding, PPAP includes capability studies, control plans, and dimensional validation. When I helped a customer transition from prototype molds to 4-cavity production, we validated each cavity’s capability index (Cpk) to ensure uniformity.
Typical PPAP Deliverables for Silicone Parts
| Document | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Process Flow Chart | Maps every step from material loading to packaging |
| Control Plan | Lists parameters, CTQs, and reaction plans |
| Capability Study (Cpk/Ppk) | Proves process stability |
| First Article Inspection (FAI) | Confirms dimensional compliance |
A successful PPAP run not only validates tooling and process stability but also becomes the reference for ongoing production audits.
Measurement and Sampling Plan?
Incorrect sampling or measurement frequency hides real problems. A clear plan ensures data represents the true process.
Measurement and sampling plans define how data is collected, analyzed, and used to control process variation.

In one project, we missed early signs of shrinkage drift because we only measured every tenth part. After revising the plan to measure the first five parts of every run, we detected the root cause earlier — a heater control fluctuation.
Sampling Plan Example
| Production Stage | Sample Size | Frequency | Inspection Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| First article | 5 pcs per cavity | Each mold setup | Full dimension |
| In-process | 3 pcs per hour | Continuous | Key CTQs only |
| Final audit | 10 pcs per lot | Each batch | Visual + Functional |
FAQ: How to Select Sample Size?
Sample size depends on process stability and risk level. For new molds or unstable processes, larger samples help identify variation faster. Once the process stabilizes, sampling can be reduced per statistical control limits (e.g., Cp/Cpk ≥ 1.67).
Change and Risk Control?
Even small changes can shift process behavior. Without formal control, product consistency is at risk.
A change and risk control system ensures that adjustments or supplier changes do not compromise validated processes.

During a silicone nipple project, we changed pigment supplier without validation. The curing rate slowed down, causing short shots. Since then, I always follow a formal change review before any modification.
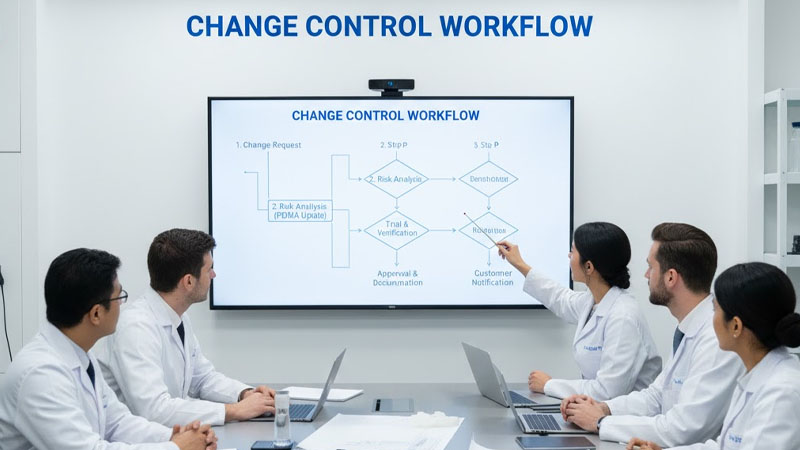
Change Control Workflow
| Step | Description | Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Change request submission | Process engineer |
| 2 | Risk analysis (FMEA update) | Quality & Engineering |
| 3 | Trial and verification | Production |
| 4 | Approval and documentation | Management |
| 5 | Customer notification | Project manager |
Risk control is not about avoiding change but managing it responsibly. Each approved change should include a verification plan to recheck CTQs and process capability.
Conclusion
Ready to stabilize your silicone production process?
Submit your critical dimensions and performance indicators to receive a custom control plan draft from our process engineering team at RuiYang Silicone.