Folding silicone products are designed to be flexible — but flexibility alone doesn’t guarantee durability. After hundreds or thousands of folds, cracks, whitening, and seal failures often appear.
Optimizing wall thickness, rib geometry, and hinge radius ensures silicone folding structures achieve long-term fatigue resistance without sacrificing usability or aesthetics.

When I developed a collapsible lunch box for a client, the first prototype failed after only 300 folding cycles. By redesigning rib geometry and hinge radii, the lifespan extended beyond 3000 cycles. Here’s what that process taught me.
Use Cases and Lifespan Goals?
Different products have very different fatigue requirements. A foldable cup used once daily isn’t the same as a collapsible lunch box folded multiple times a day.
Defining folding frequency, environment, and failure modes is the first step to designing for fatigue resistance.

Typical Folding Frequency and Lifespan Targets
| Use Scenario | Daily Frequency | Target Lifespan | Typical Failure Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Portable cup | 1–2 folds/day | ≥500 cycles | Whitening, minor deformation |
| Lunch box | 3–5 folds/day | ≥1000 cycles | Seal failure, hinge tear |
| Storage container | 10+ folds/day | ≥3000 cycles | Crack at folding seam |
Common Failure Modes
- Tearing: Starts at thin or sharp corners.
- Whitening: Caused by local stress concentration exceeding elastic strain limit.
- Permanent deformation: Silicone “sets” under repeated strain.
- Seal failure: Compression set in sealing lip areas.
By defining lifespan expectations early, designers can align structural and material choices with realistic fatigue performance.
Thin Wall and Rib Layout?
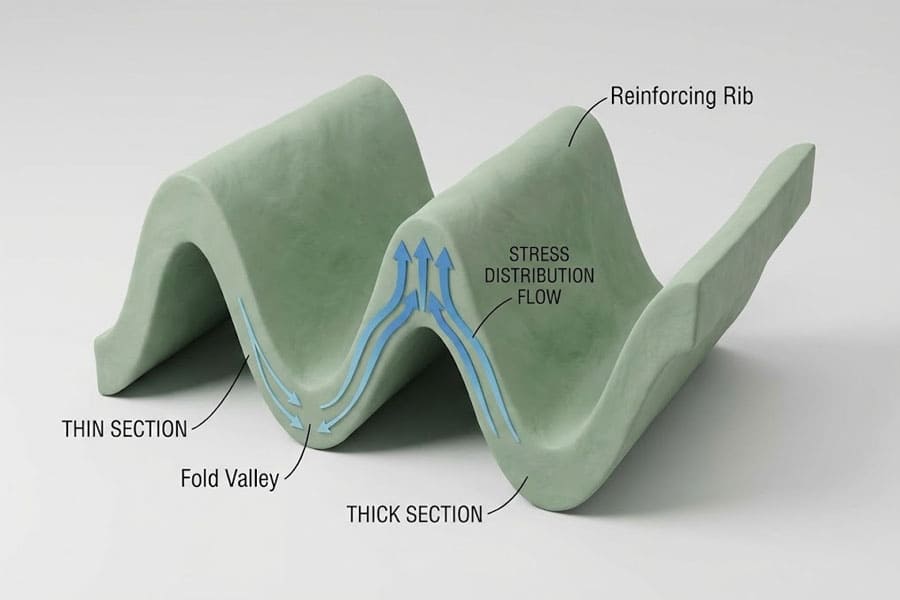
Wall and rib design directly determine how stress distributes across folding zones. Too thick, and the hinge resists folding. Too thin, and it tears prematurely.
Balanced wall thickness and rib geometry minimize stress concentration while preserving folding flexibility.
Recommended Wall Thickness (Based on Silicone Hardness)
| Hardness (Shore A) | Min Wall (mm) | Typical Wall (mm) | Max Wall (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20A | 0.5 | 0.8 | 1.5 |
| 40A | 0.8 | 1.2 | 2.0 |
| 60A | 1.2 | 1.8 | 2.5 |
Rib Design Guidelines
| Design Element | Recommended Range | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Rib height | 0.3–0.5× wall thickness | Reinforce fold area |
| Rib spacing | ≥3× wall thickness | Even stress distribution |
| Transition radius | ≥0.2 mm | Avoid sharp stress risers |
| Fold alignment | Centered along rib valley | Promote symmetric bending |
Filleted transitions and gradual thickness variation reduce localized strain. In folding areas, a thinning ratio of 60–70% (relative to base wall thickness) helps distribute bending stress evenly.
Hinge and Fold Radius Design?
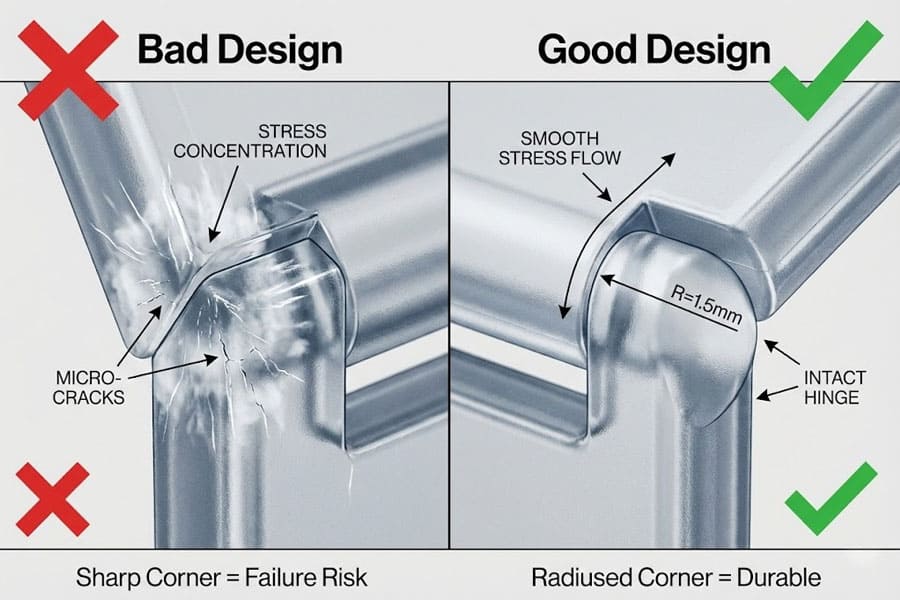
Hinge geometry defines how silicone bends — too tight a radius leads to whitening or micro-cracks, while too large reduces fold compactness.
Calculating the proper bending radius and hinge type ensures a smooth, long-lasting folding motion.
Minimum Bend Radius Formula
\[ R_{min} = k \times t \]
Where:
- Rmin = minimum inner bend radius
- t = wall thickness
- k = material factor (depends on hardness)
| Hardness (Shore A) | k Factor | Minimum Bend Radius (for 1 mm wall) |
|---|---|---|
| 20A | 1.0–1.2 | 1.0–1.2 mm |
| 40A | 1.5–2.0 | 1.5–2.0 mm |
| 60A | 2.5–3.0 | 2.5–3.0 mm |
Hinge Design Types
| Hinge Type | Structure | Benefit | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Living hinge | Continuous thin section | Simplest, cost-effective | Single-fold cups |
| Film hinge | Gradual thickness taper | Better strain distribution | Multi-layer folds |
| Dual-radius hinge | Two-step curve | Smooth rebound | Collapsible containers |
Pre-set creases or guiding ribs can help folding occur in predictable lines, preventing uncontrolled deformation and premature fatigue.
Material and Hardness Selection?
Silicone hardness affects both flexibility and fatigue strength. Selecting the right grade and additives makes the difference between lasting 300 cycles and 3000.
Choosing appropriate silicone hardness, additive package, and dual-hardness design maximizes folding endurance.

Hardness vs. Fatigue Life
| Hardness (Shore A) | Folding Endurance (Cycles) | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| 20A | ~2000 | Flexible cup walls |
| 30A | ~3000 | General folding zone |
| 40A | ~5000 | Reinforced lunch boxes |
| 60A | ~800 | Stiff support frame |
Other Material Considerations
| Factor | Description | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Food-grade vs. industrial silicone | Food-grade offers safer chemistry but slightly lower tear strength | Adjust geometry for compensation |
| Toughening agents | Improve tear resistance 20–30% | Use in folding zones |
| Dual-hardness co-injection | Combines rigid frame with soft hinge | Best for structural foldables |
FAQ: What Are the Costs and Advantages of Dual-Hardness Design?
Dual-hardness molding increases tooling cost by 20–30% but delivers over 2–3× fatigue life improvement. It also allows tight sealing while keeping fold zones flexible — ideal for premium, long-life designs.
Fatigue Validation and Failure Analysis?
No design is complete without verification. Folding fatigue tests and FEA simulations identify weak points before production.
Fatigue testing and virtual analysis ensure folding designs meet life goals under real and accelerated conditions.

Typical Testing and Validation Methods
| Test | Description | Evaluation Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Folding cycle test | 0–180° folding at set speed | Failure cycle count |
| FEA strain simulation | 3D model under bending | Max strain ≤ 20% |
| Accelerated aging | 70°C × 1000 h + humidity | Post-aging life retention ≥ 80% |
| Visual analysis | Whitening, cracks, deformation | Failure mode documentation |
Typical Failure Mechanisms
- Whitening: Polymer chain orientation and micro-crack initiation.
- Tearing: Excessive strain in hinge root or sharp rib.
- Seal degradation: Compression set after repeated thermal cycles.
- Permanent set: Crosslink fatigue after long-term folding.
Why Does Whitening Occur?
Whitening results from micro-voids and polymer chain alignment caused by repeated strain beyond the elastic limit. Softer silicones or larger bend radii reduce whitening tendency.
Conclusion
Fatigue-resistant silicone design is about harmony — between structure, material, and geometry. By managing thickness, radius, and hardness, designers can achieve foldable products that last thousands of cycles without losing shape or seal integrity.
Want to verify your folding design before tooling?
Submit your structural sketches and lifespan goals to our team for a custom design verification checklist, or download the Folding Structure Design Specification Quick Reference from RuiYang Silicone.