Silicone extrusion molding is one of the most reliable and widely used processes in modern industry. From medical tubing that saves lives to weather seals that keep your car doors from rattling, this process is quietly working behind the scenes to make our daily lives smoother. So, how does a soft, dough-like material transform into perfectly shaped, high-performance products? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of silicone extrusion molding and break it down step by step.
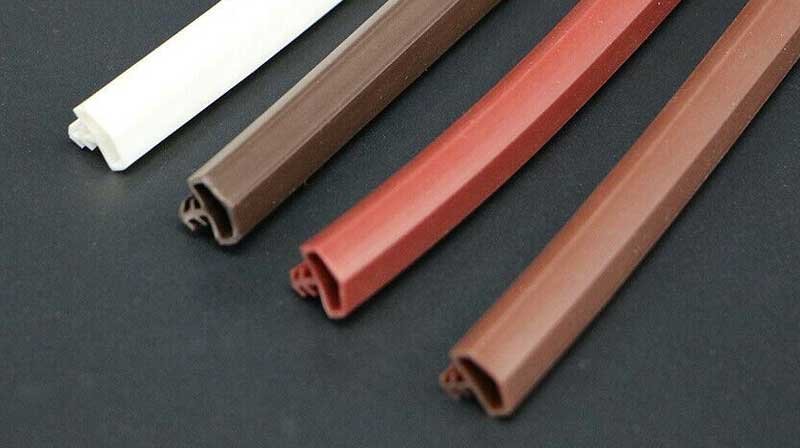

What Is Silicone Extrusion Molding?
The silicone extrusion process is a silicone manufacturing technique. To begin with, it heat and force material through a die to create the desired shape. After extrusion, the material undergoes a curing process to enhance its durability and heat resistance. Finally, the product is cooled, cut, and prepared for further use. This efficient process is widely used to produce precise, high-quality silicone products for various industries.
Process of Silicone Extrusion Molding
The silicone extrusion process is a well-established method used to produce a wide range of silicone products. It involves several stages that transform raw silicone material into high-quality extrusions suitable for various industries. Below is a detailed explanation of each step in the process.
Material Preparation
The silicone extrusion process begins with the preparation of materials. High Consistency Rubber (HCR) is commonly used due to its strength and versatility. Besides, depending on the final product’s requirements, additives are also chosen. The additives are as follows.
- Curing Agent: These include peroxide or platinum-based catalysts, used for curing during the extrusion process.
- Filler: To adjust properties of silicone, fillers like silica or other compounds are added. These can improve tensile strength, reduce shrinkage, or adjust hardness.
- Pigment: Pigments are incorporated to comply with specific product requirements.
- Other Additives:Plasticizers enhance flexibility, while stabilizers improve resistance to aging and environmental factors.
Mixing
Once the materials are prepared, they are ready for mixing. Mixing is the process of blending the silicone with additives to create a uniform compound, ready for extrusion. This is typically done using specialized equipment like a two-roll mill or an internal mixer.
- Two-roll Mills: Two-roll mills are used to mix materials more evenly. The rolls pass the materials through, mixing and shearing them continuously.
- Internal Mixer: A two-roll mill or Banbury mixer is used to blend the silicone base with additives. The materials are kneaded until it reaches the right consistency.
- Dispersion of Additives: Proper dispersion is essential. Additives are thoroughly mixed to ensure they are evenly distributed throughout silicone, providing the desired properties like strength, elasticity, and thermal stability.
- Viscosity Adjustment: Viscosity is carefully adjusted during this process to ensure that the silicone will flow smoothly through the extruder without being too thick or too thin.
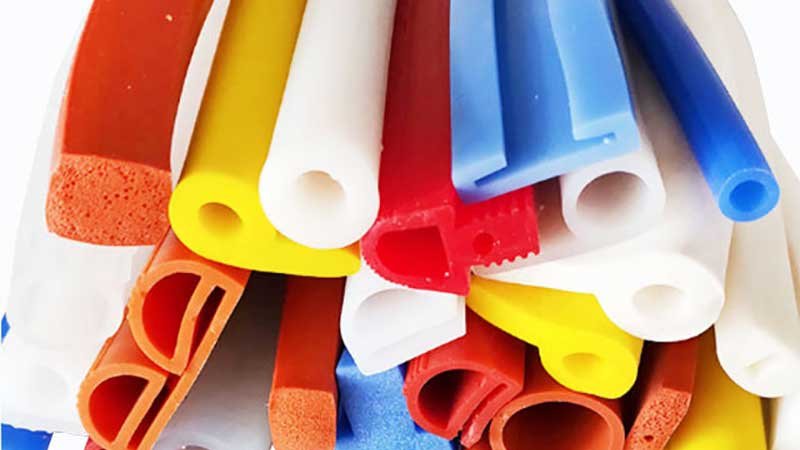

Extrusion
The extrusion starts by feeding the prepared silicone material into an extruder. The material is heated, pressurized, and forced through a die to shape it into the desired profile.
Extrusion Process:
The extruder consists of a heated barrel and a rotating screw. The screw pushes the material forward while gradually heating it. The temperature of the extruder is carefully controlled to maintain the appropriate consistency and flow of the silicone material.
The material is then forced through a die to shape the product. The material needs to flow smoothly and uniformly through the die to avoid defects such as bubbles, inconsistent thickness, or surface irregularities.
Curing
After the silicone is extruded, it undergoes vulcanization, a curing process that turns the rubber from a soft, flexible state into a solid, durable material.
Curing Process:
The extruded silicone passes through a heated curing oven, where the material is exposed to high temperatures, usually between 160°C-200°C. Then, the curing agent reacts with the silicone polymer, creating crosslinks between the chains. This makes the material strong and resistant to heat and wear. The curing time can vary depending on the thickness of the extruded material.

Post-Processing
Several post-processing steps need to be done to ensure the product meets the desired specifications.
- Cooling: After curing, the material needs to be cooled to stabilize its structure. This is typically done using air cooling or water baths. Rapid cooling can help solidify the product and prevent it from deforming.
- Cutting: The continuous extruded material is often cut into specific lengths or sections according to customer requirements.
- Spooling: For products like silicone tubing, the material is wound onto spools for easier handling and transport.
Some silicone products may require additional processes such as bonding, printing, or assembling.
- Bonding: Silicone parts might be bonded with other materials to create multi-functional products.
- Printing: Logos, part numbers, or other markings may be printed on the surface of the product.
- Assembly: Some silicone products may need to be assembled into larger units, like silicone gaskets or seals.
Quality control is important in ensuring that the final product meets all necessary specifications.
- Each batch of extruded silicone undergoes various tests, including tensile strength, elongation, and hardness.
- Visual inspections are conducted to detect defects like bubbles or irregular surfaces.
- Dimensional is measured with calipers or laser systems to ensure that the products meet the required sizes and tolerances.
Advantages of Silicone Extrusion Molding
High Precision and Consistency
Extruded silicone products are known for their consistent quality and precise dimensions. The process ensures that each batch maintains uniform thickness, shape, and material distribution. Even complex cross-sectional profiles can be achieved with ease.
Versatility in Design and Application
A wide range of shapes, sizes, and designs can be produced, from simple tubes to intricate sealing profiles. Silicone extrusions are widely used in medical, automotive, electronics, and industrial applications. Customization options, such as color variations and material modifications, are readily available.
Efficient and Cost-Effective for Large Volumes
Once the extrusion setup is complete, the process runs continuously, making it ideal for high-volume production. Besides, material waste is minimized, as silicone is used efficiently in the extrusion process. Moreover, automation reduces labor costs and increases manufacturing speed.
Limitations of Silicone Extrusion Molding
Silicone extrusion molding offers many benefits, but it’s not ideal for every project. Here’s what to consider before choosing this method.
Initial Setup Can Be Time-Consuming and Expensive
Designing and testing custom dies takes time, especially for unique shapes. Tooling can be costly, particularly for small batch orders. In many cases, multiple adjustments are needed to fine-tune extrusion parameters and achieve the desired output.
Only Suitable for Continuous Profiles
Extrusion works best for producing straight, continuous shapes like tubes, cords, or strips. It cannot create complex 3D parts on its own. Producing more intricate designs usually requires additional forming or assembly after extrusion.
Often Requires Post-Processing
Extruded silicone parts may need to be cut, bonded, or further cured after initial shaping. Surface finish options are also limited compared to injection molding. Maintaining consistent tolerances throughout production can be challenging and requires strict quality control.
While extrusion is efficient for many applications, understanding these limitations helps ensure the process aligns with your product goals.
Applications of Silicone Extrusion Molding
Silicone extrusion molding is widely used across various industries. Its ability to produce continuous, flexible, and durable profiles makes it a preferred choice for many applications. The following table lists some industries using silicone extrusion and suitable properties for these applications.
| Industry | Applications | Key Characteristics |
| Medical | Tubing, catheters, seals, gaskets, peristaltic pump tubes | Biocompatible, sterilizable, flexible, non-toxic |
| Automotive | Seals, gaskets, hoses, vibration dampeners | Heat-resistant, weatherproof, durable |
| Electronics | Insulation, wire coatings, EMI shielding | Electrical insulation, temperature stability |
| Aerospace | Sealing strips, thermal insulation, vibration damping | Lightweight, high-temperature resistant, ozone-resistant |
| Construction | Window seals, weatherstrips, expansion joints | UV-resistant, waterproof, long-lasting |
| Food & Beverage | Food-grade tubing, seals, gaskets | FDA-approved, non-toxic, resistant to extreme temperatures |

Market Analysis of Silicone Extrusion Molding
The silicone extrusion molding market has experienced steady growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across industries such as healthcare, automotive, electronics, and construction. The global market size is projected to expand further as industries seek high-performance materials that offer durability, flexibility, and resistance to extreme conditions. With advancements in material formulations and manufacturing technologies, the market is expected to witness innovation in product customization and efficiency.
In terms of competition, the industry is dominated by key players that hold significant market shares through strong R&D capabilities, advanced production techniques, and well-established supply chains. Leading companies focus on product quality, innovation, and strategic partnerships to maintain their competitive edge. Meanwhile, emerging enterprises are finding opportunities in niche markets by offering specialized solutions, cost-effective production, and sustainable alternatives. As demand continues to grow, competition will intensify, encouraging further technological developments and expansion into new application areas.
Conclusion
Silicone extrusion molding may not be the flashiest process out there, but it’s certainly one of the most effective. It combines precision, efficiency, and versatility. Whether it’s heat-resistant automotive gaskets, flexible medical tubing, or food-safe kitchenware, extruded silicone is everywhere, quietly proving its worth. As technology continues to advance, this process will only become more refined, opening doors to even more innovative applications. In short, silicone extrusion molding is not just a manufacturing technique—it’s a gateway to durable, high-performance products that improve our everyday lives.