Silicone is known for its versatility, used across industries from automotive to medical devices. But when it comes to choosing the right type of silicone, Shore hardness is a key factor. Why? Because it directly affects the material’s flexibility, durability, and performance in specific applications. Understanding the right Shore hardness for your project can mean the difference between success and failure.
Shore hardness is a measure of a material’s resistance to indentation. In silicone, this property determines how flexible or rigid the material will be. The higher the Shore hardness, the more resistant the material is to deformation. Conversely, lower Shore hardness means the material is softer and more flexible.
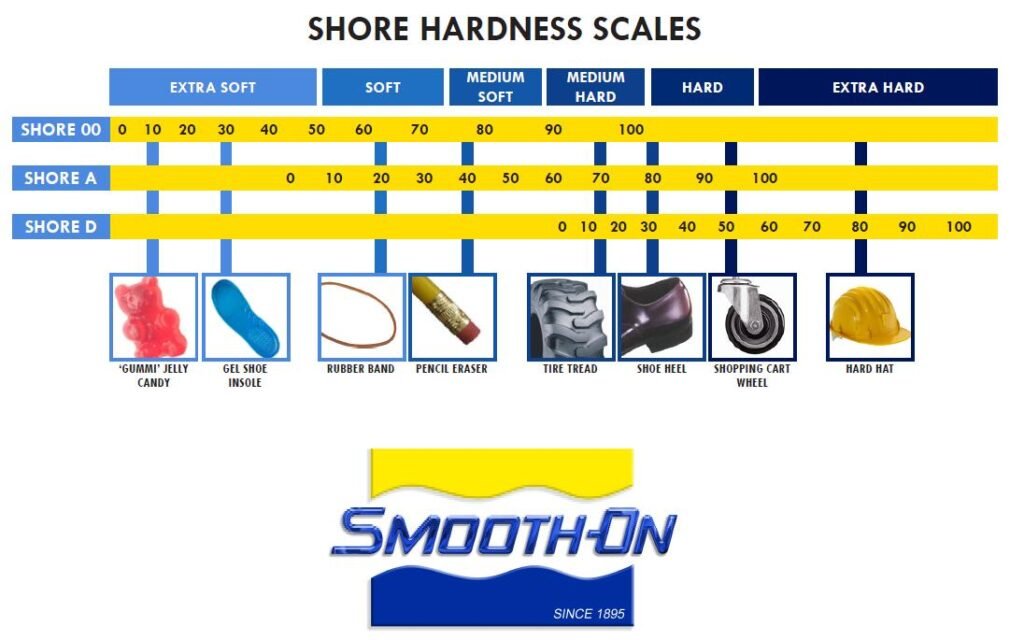
What is Silicone Shore Hardness?
Shore hardness is determined using a device known as a durometer. This tool applies a specific force to the silicone and measures the depth of the resulting indentation. The measurement is expressed on various scales, each suited for different types of materials.
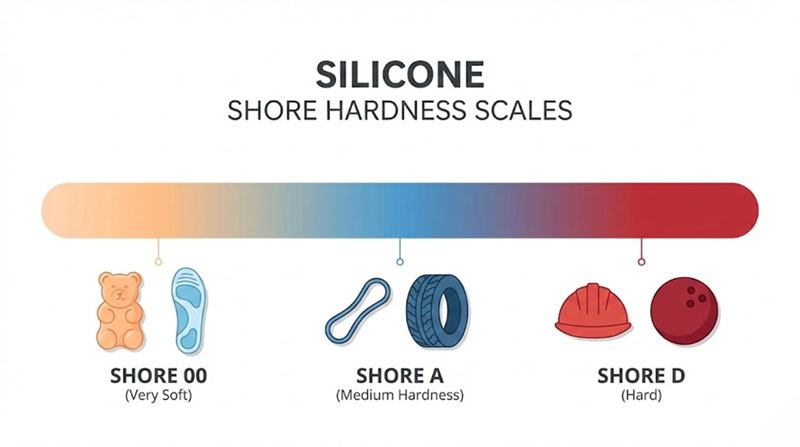
Shore OO Scale
The Shore OO scale is reserved for very soft materials, such as gels and foams. This scale measures the softness of silicones that require high flexibility and cushioning properties. Products like soft grips, padding, or certain medical implants are tested on the Shore OO scale to guarantee their softness and performance.
Shore A Scale
The Shore A scale is used for measuring the hardness of softer materials. It is commonly applied to silicones used in products that require flexibility, such as seals, gaskets, and certain medical devices. This scale helps manufacturers ensure that these softer materials will perform effectively in their intended applications.
Shore D Scale
The Shore D scale is designed for harder materials. This scale is typically used for silicones that need to be more rigid and durable, such as those used in structural components or industrial applications. The Shore D scale ensures that these harder materials can withstand greater stresses and maintain their integrity over time.
How Does Shore Hardness Impact Silicone Applications?
Shore hardness plays a vital role in determining the suitability of silicone for various applications across different industries. Here’s how it impacts some key sectors:
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, silicone with medium to high Shore hardness is crucial for components like seals and gaskets. These parts must endure extreme temperatures and pressures, requiring a material that offers both durability and resistance to deformation.
Medical Field
In the medical field, softer silicones with lower Shore hardness are often preferred. These materials are ideal for implants and catheters, where flexibility and biocompatibility are essential. The softness ensures patient comfort while maintaining the necessary performance characteristics.
Electronics Industry
In the electronics industry, the Shore hardness of silicone influences its use in insulation and protective components. Silicone with the appropriate hardness ensures that electronic parts are shielded from environmental factors, such as moisture and dust, while maintaining the necessary flexibility.
Consumer Products
For consumer products, the right Shore hardness can enhance the tactile feel, durability, and overall performance of items like kitchen utensils and personal care products. Silicone’s versatility allows it to be tailored to the specific needs of each product category.
What Factors Affect Shore Hardness Accuracy?
Several key factors can influence the accuracy of Shore hardness measurements. Understanding these factors is essential for obtaining reliable results, especially when comparing different silicone products.
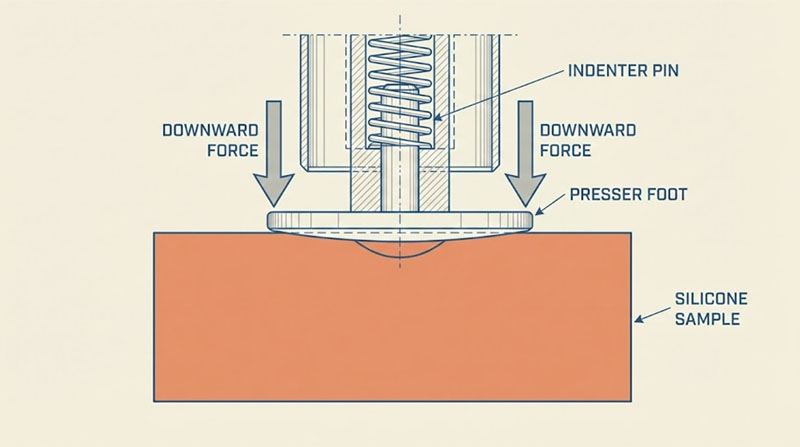
Thickness of the Specimen
The thickness of the silicone specimen is critical. If the material is too thin, the readings can be inaccurate, as the durometer might not fully engage with the material. A standard thickness of at least 6 mm is recommended to ensure precise measurements.
Temperature Conditions
Temperature plays a significant role in Shore hardness accuracy. Testing should be conducted at a standard temperature of 23 ± 2 °C. Deviations from this temperature can cause the material to harden or soften, leading to skewed results.
Speed of Force Application
The speed at which the force is applied with the durometer can also introduce variability. Applying the force too quickly or too slowly can affect the indentation depth, resulting in inconsistent readings. Maintaining a consistent application speed is crucial for accurate measurements.
How Does Silicone Compare to Other Materials?
When selecting materials for your project, it’s crucial to consider how silicone stacks up against other options like thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) or metals. Shore hardness plays a significant role in this decision-making process. To help illustrate the differences, here’s a comparison table:
| Material | Shore Hardness | Chemical Resistance | Temperature Stability | Flexibility | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicone | Varies (Shore A, D, OO) | Superior | Excellent (wide range) | High | Seals, gaskets, medical devices, electronics |
| TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomers) | Varies (Shore A, D) | Moderate | Good (limited range) | Moderate to High | Tubing, seals, consumer products |
| Metals | High (Rigid) | Limited | Excellent (narrow range) | Low (Rigid) | Structural components, mechanical parts |
As you can see, silicone generally excels in chemical resistance and temperature stability, maintaining its properties across a broad range of conditions. This makes it ideal for applications where durability and flexibility are crucial. In contrast, TPE offers good flexibility but may not perform as well in extreme conditions. Metals, while strong and rigid, lack the flexibility that many applications require, making silicone a better choice where elasticity and resilience are needed.
How to Choose the Right Silicone Hardness?
Picking the right silicone hardness isn’t random. It depends on how the product will be used, how it should feel, and how it needs to be made. Just like choosing shoe soles. Some need to cushion and others need to support.
Here’s a guide to picking the right hardness based on different uses.
Skin-Contact Products: Prioritizing “Skin-Friendly” Feel
For products that touch the skin, comfort and safety come first.
The recommended silicone hardness usually falls between 10A and 40A, sometimes even as soft as Shore 00.
Baby products like pacifiers, teethers, and nasal aspirators typically use silicone in the 20A to 30A range. This softness mimics the feel of skin and ensures safety and comfort for babies’ delicate mouths and skin.
Medical devices, such as catheters, respiratory masks, and prosthetic liners, have a broader hardness range from 10A to 50A depending on their function. For example, catheters often require a softness around 20A to provide flexibility, while prosthetic liners may need up to 50A to offer light support. Some ultra-soft scar patches even use Shore 00 silicone to achieve the maximum softness and conform closely to the skin.
Wearable devices like smartwatch straps and earphone tips generally fall between 30A and 50A. This range balances comfort and stability—too soft can feel loose, while too hard may cause discomfort.

Daily Consumer Goods & Kitchenware: Balancing Function and Feel
Daily consumer goods and kitchenware require silicone that is practical, durable, and comfortable to use.
The recommended hardness range for these products is generally between 40A and 70A.
Kitchenware items such as spatulas, baking molds, and lids usually use silicone from 40A to 60A. This range is tough enough to handle stirring and cooking tasks, while still flexible enough for easy use. Molds also need to release food easily and maintain their shape well.
Device protectors, including phone and tablet cases or remote covers, typically fall within the 40A to 60A range. This hardness level offers enough softness for shock absorption and grip, while being firm enough to keep their shape.
Household items like toothbrush handles, placemats, and cup lids vary from 40A to 70A, depending on the needed grip, texture, and support.
Industrial Applications: Emphasizing Performance and Environmental Adaptation
Industrial silicone must handle pressure, heat, vibration, and wear.
The recommended hardness here ranges from 50A to 90A, with Shore D used for more rigid parts.
Seals such as O-rings, gaskets, and sealing strips commonly have hardness between 50A and 70A. They need the right hardness to maintain a tight seal under pressure and avoid leaks, and higher hardness is preferred for harsh environments.
Damping pads and buffers usually fall between 50A and 65A, offering enough softness to absorb shock while remaining strong enough to resist deformation.
Cable insulation and electrical potting materials vary widely in hardness, depending on their function, but focus on insulation, heat resistance, and durability.
Industrial rollers and conveyor belts often require hardness of 70A or higher, sometimes even Shore D, to provide excellent strength, abrasion resistance, and stability under heavy loads.

Structural Components & Composite Materials: Hardness for Support
When silicone is part of a structure or layered with other materials, it must stay firm and stable.
For these applications, the recommended hardness is 70A or above, or Shore D.
Hard buttons or keycaps need to offer clear tactile feedback and durability, typically using silicone with hardness between 70A and 85A.
Internal support components require even higher hardness, usually between 80A and 90A, or Shore D, to maintain shape and resist forces.
For silicone overmolding on tools or devices, hardness depends on the needed grip and function. Tool handles often use silicone with hardness between 60A and 80A, balancing comfort with strength and durability.

Why Do Industry Standards Matter?
Adhering to industry standards like ASTM D2240 for Shore hardness testing ensures consistency and reliability in results. These standards provide guidelines for specimen preparation, testing conditions, and data interpretation. Following these protocols helps manufacturers ensure that their silicone products meet required performance criteria, reducing the risk of product failure. Compliance with these standards is not just a best practice—it’s a necessity in industries where safety and performance are critical.
Conclusion
Understanding silicone Shore hardness is essential for selecting the right material for your project. It influences everything from flexibility to durability, impacting the success of your application. By following industry standards and ensuring accurate measurements, you can optimize your material selection for the best results.
We have another article about Silicone Shore A Hardness: Effects on Feel, Sealing, and Durability